Google Ads continues to be a cornerstone of digital marketing, offering advertisers a sophisticated yet accessible way to reach their target audiences. At the heart of this platform is the auction system—a behind-the-scenes mechanism that determines which ads appear for which searches, where they appear, and how much advertisers pay.
While the fundamental principles remain the same, the system has evolved significantly through advances in artificial intelligence (AI), automation, and ad formats. Here’s how it all works today.
Table of Contents
The Foundations: Keywords and Intent
Every Google Ads campaign begins with keywords—terms or phrases that advertisers believe users might type when searching for their products or services. These could be brand names, descriptive product terms, or broad concepts tied to user interest.
What has changed in recent years is the system’s ability to interpret user intent. With AI models like BERT and MUM deeply integrated into the search algorithm, Google now better understands what users are actually looking for, even when their queries are vague or complex. As a result, broad match keywords—once considered too imprecise—have become more effective when paired with smart bidding strategies. This shift allows advertisers to focus more on intent and less on creating exhaustive keyword lists.
From Search to Auction
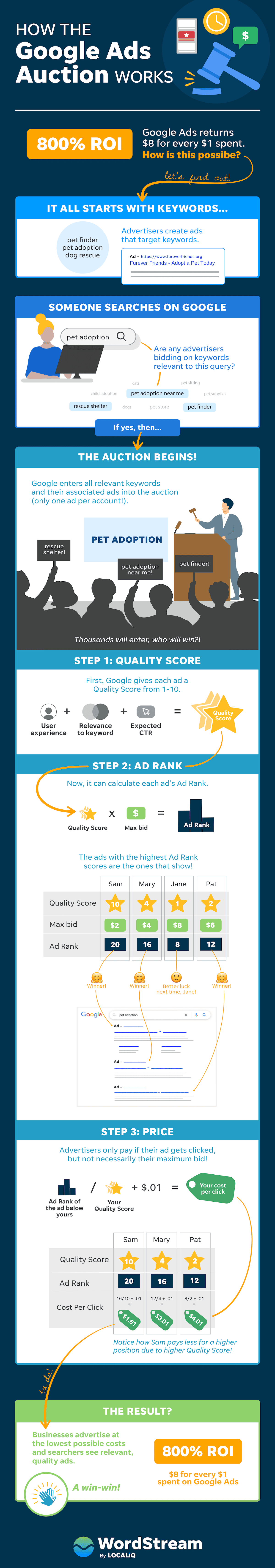
When a user enters a query, Google evaluates whether that query matches any advertiser’s selected keywords. If a match is found, an auction is triggered. This isn’t a traditional auction where the highest bid automatically wins; instead, Google uses a more nuanced formula that prioritizes user experience and ad relevance.
Evaluating Quality: What Makes an Ad Competitive
Before any ad is shown, Google assigns it a Quality Score, which is based on three primary factors:
- The expected click-through rate (CTR)
- The relevance of the ad to the search query
- The landing page experience, including mobile optimization and load speed
The Quality Score has also benefited from AI-powered predictive analytics in recent years. These tools draw on historical performance data, comparing similar audiences and devices to assess how likely an ad is to engage users. Advertisers who offer fast-loading, well-matched landing pages and tailored ad copy will typically receive higher scores.
Calculating Ad Rank and Determining Placement
Ad Rank is what ultimately decides which ads appear and in what order. It’s calculated using a combination of the advertiser’s maximum bid and the ad’s Quality Score. However, the formula has grown more sophisticated over time.
- Real-Time Signals: Ad Rank now considers dynamic factors such as user behavior, device type, location, and time of day. You can improve performance by using audience segmentation, setting device bid adjustments, and scheduling ads during high-conversion hours to align with user context and intent.
- Ad Extensions: Elements like sitelinks, callouts, structured snippets, and other extensions enhance your ad by offering more information and improving visibility. Including as many relevant extensions as possible and tailoring them to user intent can boost engagement and strengthen your Ad Rank.
- Ad Format: The type of ad—text, video, app promotion, shopping, or interactive—now plays a more prominent role in determining Ad Rank. Choosing the format that best fits your audience’s behavior and optimizing creative assets helps improve placement, especially for mobile-first or video-oriented users.
What Advertisers Pay: A Smarter Pricing Model
Contrary to popular belief, advertisers don’t necessarily pay their maximum bid. Instead, they pay just enough to outbid the next highest Ad Rank, plus one cent. This is known as the second-price auction model.
That said, pricing is now more dynamic due to the increased use of automated bidding strategies. Advertisers can choose goals like maximizing conversions, maximizing conversion value, or achieving a specific return on ad spend (ROAS). These strategies allow Google’s AI to automatically adjust bids in real time, often resulting in higher efficiency and potentially higher costs for high-value clicks.
Match Types, Targeting, and Formats
Advertisers still have control over how closely a search query must match their keywords through match types:
- Exact Match for precise targeting
- Phrase Match for a middle ground
- Broad Match for maximum reach
- Negative Keywords to filter out irrelevant traffic
Thanks to improved AI, Broad Match is now more intelligent. It identifies contextual relevance based on user intent and reduces the need for long negative keyword lists.
Beyond keywords, advertisers can refine their targeting based on demographics, location, device type, and time of day. The system also offers a variety of ad formats to suit different goals:
- App Ads: Designed to drive mobile app installations and engagement, these ads appear across Search, Play Store, YouTube, and the Display Network. Google automatically generates and places the ads based on assets provided by the advertiser, such as text, images, and video. Effective app campaigns rely on clear value propositions and a well-optimized app store listing to encourage downloads.
- Click-to-Call Ads: Tailored for mobile devices, these ads feature a call button that lets users dial a business directly from the search results. They’re particularly valuable for service-based businesses where phone leads are crucial. To maximize impact, advertisers should set these ads to appear during business hours and use call tracking to measure conversions accurately.
- Discovery Ads: A visually rich, native ad format that appears across Google’s Discover feed, Gmail promotions tab, and YouTube home feed. Discovery ads use audience signals and machine learning to present content that aligns with users’ interests before they search. They are ideal for reaching users in the awareness or consideration phase. High-quality imagery and a strong understanding of target audience preferences are key to performance.
- Display Ads: These are visual ads—typically images or rich media—that appear across the Google Display Network, which includes millions of websites, apps, and Google-owned properties like YouTube and Gmail. Display ads are ideal for brand awareness, remarketing, and reaching users during passive browsing. Success with this format depends on compelling creative, strategic audience targeting, and effective placement exclusions to avoid wasted spend.
- Performance Max (PMax) Campaigns: A fully automated campaign type that runs across all of Google’s properties—including Search, Display, YouTube, Gmail, Discover, and Maps—from a single campaign. PMax uses machine learning to optimize creatives, audience targeting, bidding, and placements based on real-time data and conversion goals. While it reduces manual control, advertisers can influence performance by supplying a variety of strong creative assets, setting clear campaign objectives, and using audience signals to guide Google’s automation effectively.
- Shopping Ads: Specifically designed for e-commerce, Shopping ads showcase product images, prices, merchant names, and more directly in the search results. They appear when users search for specific products and often include comparison features. These ads are powered by product feeds submitted through Google Merchant Center and are most effective when feeds are optimized with accurate titles, high-quality images, and competitive pricing.
- Text ads: Consist of headlines, a display URL, and description lines. They appear alongside organic results on the Google Search Engine Results Page (SERP) when users search for relevant queries. Text ads are best suited for direct-response campaigns targeting high-intent searches. Optimizing ad copy, using strong calls to action, and incorporating keyword-rich headlines can improve click-through rates and Quality Score.
- Video Ads: These ads run on YouTube and Google’s video partner sites, offering a dynamic way to engage users through storytelling, demonstrations, or brand messaging. Video ads can be skippable or non-skippable and can serve at various stages of the user journey. Success requires attention-grabbing openings, short run times for mobile users, and clear calls to action within the video or accompanying copy.
Budget and Bidding Strategies
Advertisers set daily budgets and select bidding strategies that align with their campaign goals. Traditional bidding options like cost-per-click (CPC), cost-per-mille (CPM), and cost-per-acquisition (CPA) are still available, but the trend is moving toward fully automated solutions.
Strategies such as Maximize Conversions and Target ROAS use real-time data and AI to allocate budgets where they’re most likely to generate results. Shared and portfolio budgets have also become more intelligent, distributing spend across multiple campaigns based on live performance metrics.
Auction Outcomes and Ad Delivery
Once all variables are considered—keywords, match types, targeting settings, bid strategy, Quality Score, and Ad Rank—the system determines which ads will appear and in what format. The highest-ranking ads are then delivered either on the search results page or across Google’s partner networks.
Performance Max campaigns, in particular, have redefined ad placement by merging multiple ad types into a single campaign. Google’s AI chooses the best channel, format, and creative element to meet the advertiser’s goals, simplifying management while maximizing reach.
After the Click: Tracking and Optimization
The journey doesn’t end with a click. Once the user arrives on the landing page, advertisers track key actions such as purchases, sign-ups, or downloads. These conversions inform future bidding decisions and campaign adjustments.
Advertisers review performance data to assess ROI and identify areas for improvement. They may refine ad copy, adjust keyword strategies, tweak targeting settings, or redesign landing pages to improve relevance and boost conversion rates. The continuous feedback loop ensures that campaigns become more effective over time.
The Bottom Line
The Google Ads auction system is designed to create value for users and advertisers. Users receive highly relevant ads tailored to their search behavior, while businesses benefit from a performance-driven model that helps them reach the right audience at the right time.
While previous years touted an average 800% return on ad spend, Google now emphasizes that ROAS can vary significantly depending on industry, strategy, and campaign type. What remains constant is the opportunity for well-structured, intelligently optimized campaigns to deliver strong results in a competitive marketplace.
By understanding how the auction system works and how it has evolved with AI, automation, and new ad formats, advertisers can create campaigns that not only perform well but also adapt quickly to changing user behavior and market dynamics.